Chlorophyll is widely present in higher green plants such as fruits and vegetables, and is combined with proteins into chloroplasts. There are two types of chlorophyll in higher plants: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Both chlorophylls are soluble in organic substances such as ethanol, ether and acetone. Chlorophyll is an essential factor for the photosynthesis of green plants and plays a role in absorbing and transmitting light energy in photosynthesis. The molecular formula of chlorophyll a is C40H70O5N4Mg. The molecular structure of chlorophyll a is linked by 4 pyrrole rings through 4 methylene groups (=CH-) to form a ring structure called porphyrin (side chain on the ring). At the center of the porphyrin ring, there is one magnesium atom and one cyclopentanone (V). The propionic acid on the ring IV is esterified and saponified by phytosterol (C20H39OH) to form a water-soluble potassium salt. In an acidic environment, the magnesium in the porphyrin ring can be replaced by H, called chlorophyllin, which is brown. When the copper is replaced by copper or zinc, the color turns green again. The pigment is stable and does not fade under the light. Also, it is not destroyed by acid. The preservation of impregnated plant specimens is to use this feature. The determination of chlorophyll a using a spectrophotometer is the most common method of measuring chlorophyll a. Using a spectrophotometer, the absorbance value of the chlorophyll extract at the maximum absorption wavelength was first determined, and the chlorophyll a had the largest absorbance at 645 nm and 665 nm. Then use the Lambert-Beer law to calculate the content of each pigment in the extract. The mathematical expression of Lambert-Beer's law is A=lg(1/T)=Kbc , where A is the absorbance; T is the transmittance, which is the ratio of the incident light intensity to the incident light intensity; c is the concentration of the light-absorbing substance; b is Absorber thickness. Determination of chlorophyll a First introduce the instruments we will use in the measurement process: spectrophotometer, balance, mortar, brown volumetric flask, small funnel, quantitative filter paper, blotting paper, rubbing paper, dropper; prepare a few fresh plant leaves Prepare 96% ethanol (or 80% acetone), quartz sand and calcium carbonate powder. Then the specific operation is as follows: take fresh plant leaves (or other green tissue) or dry materials, wipe the surface of the tissue to remove dirt, and remove the midribs. Weigh 2g of freshly cut sample and place it in a mortar. Add a small amount of quartz sand and calcium carbonate powder and 3mL of 95% ethanol. Grind it into a homogenate, add 10mL of ethanol, and continue grinding until the tissue turns white. Let stand 3~5min. One filter paper is placed in a funnel and moistened with ethanol. The extract is poured into a funnel along a glass rod. The filtrate is discharged into a 100 mL brown volumetric flask. The mortar, pestle, and residue are rinsed with a small amount of ethanol several times and finally together with the residue. Pour into the funnel. Ethanol was sucked with a dropper and all the chloroplast pigments on the filter paper were washed into a volumetric flask. Until there is no green in the filter paper and residue. Finally, make up to 100 mL with ethanol and shake well. The chloroplast pigment extract was measured for absorbance at wavelengths of 665 nm, 645 nm, and 652 nm, and 95% ethanol was used as a blank control. Then, according to the calculation method of chlorophyll a provided on the data, the chlorophyll a content of the fresh plant leaves can be calculated. The specific formula is as follows: Chlorophyll a=(12.7A665-2.69A645)*(V/1000W) Chlorophyll b=(12.7A645-2.69A665)*(V/1000W) Total Chlorophyll a=(20.0A645+8.02A665)*(V/1000W) or Total Chlorophyll a=(A652/34.5)*(V/1000W) Spectrophotometer Another Method for Determination of Chlorophyll-a - Fluorescence Spectrophotometry In recent years, the spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll a in seawater has been gradually replaced by a simpler and more sensitive extraction fluorescence method. The principle is that the acetone extract of chlorophyll a is excited by blue light to generate red fluorescence. The fluorescence value of the extract before and after acidification is measured with a fluorimeter at 670 nm. The chlorophyll a content of seawater is calculated as follows: In the formula, the fluorescence value before Rb-acidification, the fluorescence value after Ra-acidification, and the acidification factor of R-pure chlorophyll a (varies with the instrument). Because of this, (1) becomes: In the formula, there are several methods for determining the conversion factor (mg/m3) of the fluorometer's measuring range during Fd-measurement. The details are as follows: (1) Standard chlorophyll-a calibration method: The mother liquor is diluted with a solution of pure chlorophyll-a, and the mother liquor is diluted into a series of solutions with different concentrations and fluorescence readings are measured. Finally, the slope of the calibration line, Fd, is calculated by a linear regression method. (2) Spectrophotometer calibration method: take a certain volume of unicellular algae in the exponential growth phase and measure the chlorophyll a spectrophotometrically. Measure the absorbance E, according to the formula chl-a = 11.85E664-1.54 E647-0.08 E630 = Cchl-a calculates the Cchl-a of this extract. Then it is measured on the fluorometer fluorescence value Rb, according to formula (3) to obtain Fd. This experiment uses a spectrophotometer correction method. Medical Connector,Industrial Ethernet Connectors,Industrial Camera Connector,Industrial Automation Connectors Dongguan Shangjie Precision Hardware Co., Ltd , https://www.shangjiecnc.com
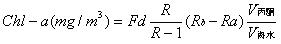 (1)
(1) 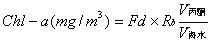 (2)
(2) 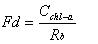 (3)
(3)