Many friends asked how to exchange visits between two computers on different network segments. This is usually encountered in the corporate office, we look at it today.
We often encounter enterprises with the increase of employees or departments, adding a router, divided into two network segments, A subnet and B subnet are on different network segments. When there are multiple routers in the network, different routers are required. Subordinate subnets can communicate with each other and at the same time can access the Internet through a broadband router. How is this achieved?
Case scenario 1
The enterprise accesses the Internet through a router R1, LAN LAN1. Because of business needs, a router R2 was expanded and a new LAN segment LAN2 was added. To enable PC1 and PC2 to communicate with each other, you can do the settings as shown in the figure below.
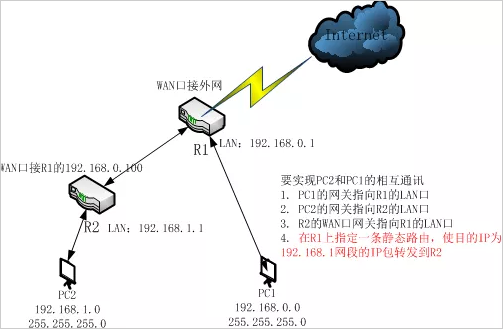
To achieve mutual communication between pc1 and pc2, you can do the following settings:
1, pc1's gateway points to R1 LAN
2. The gateway of pc2 points to the LAN port of R2.
3. R2's WAN port gateway points to the R1 LAN port.
4. Specify a static route on R1 to forward the ip of the destination ip to the 192.168.1.x network segment to R2.
Here, the R1 static route configuration is described separately: a static route is generally composed of three parts, the destination IP address, the subnet mask, and the next hop (gateway) address. According to the analysis in the above figure, the information contained in a static route is newly created. , should have the following content, the next hop address of the IP packet (subnet mask is 255.255.255.0) sent to the destination address 192.168.1.0 network segment is 192.168.0.100. The specific configuration location, if it is in the router, to TP -Link for example, in the router configuration interface, there is a static routing table configuration:
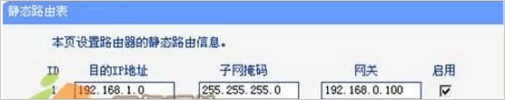
When setting a static route, the gateway IP address must belong to the same network segment as the LAN port IP address of the router. If the destination IP address is the IP address of a host, the subnet mask must be 255.255.255.255. If it is on the server, you can configure static routes through the command line, including adding, deleting, and modifying.
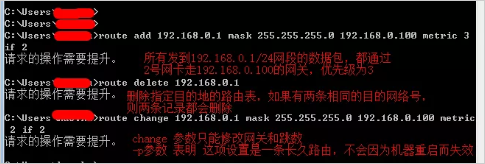
It can be seen that Case 1 is actually similar to the bridging principle of routers.
Case scenario 2
In the shared broadband access of the cell, the A user constructs a local area network with a broadband router, and the B user also constructs a local area network with a broadband router. The hosts between the A and B users' respective local area networks cannot communicate with each other. The network topology is as follows:
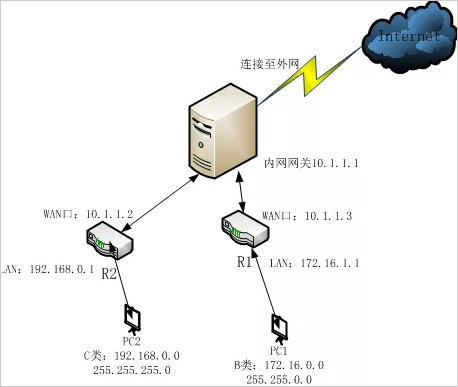
To achieve mutual access between PC2 and PC1, it seems to be somewhat similar to Case 1, and two static routes need to be added to the intranet gateway. The general cell gateway certainly does not allow users to configure routing, and after this configuration, computers on other network segments can also access PC1 and PC2.
Two routers, different network segments to access each other: Set the WAN port of the two routers to a subnet, as shown above. Router 1 WAN port ip: 10.1.1.3, router 2 WAN port ip: 10.1.1.2. The LAN ports of the two routers can be set as long as they are not in the subnet with the WAN port.
Case scenario 3
In the above case, both Case 1 and Case 2 are for two routers. For an environment with multiple routers and multiple levels of routing devices in the network, this situation can be said to be the integration of scenario 1 and scenario 2.
A similar network topology is as follows: three routers
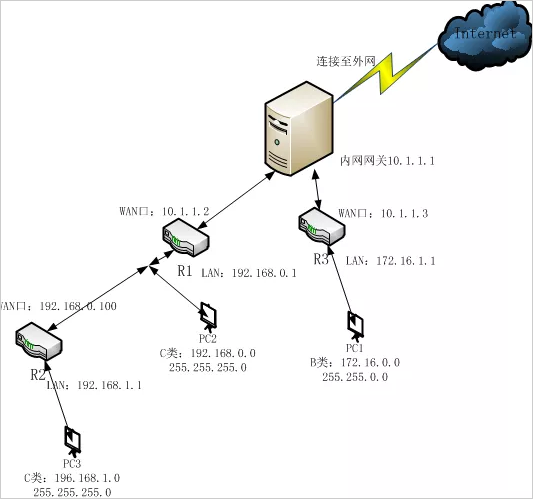
To achieve mutual access between PC1, PC2 and PC3, you need to configure Router 1 and Router 3 to configure static routes. How do you match this? In fact, the case 1 and case 2 above are integrated, which is case 3.
Analysis: (The router here is represented by R)
R1 is in the middle of R2 and R3, and R1 itself is connected to pc2. Then, to achieve mutual access between pc2 and pc1 and pc3, the destination address of R1 is pc1 and pc3.
The next hop of R1 is R2 and R3, and the WAN port of R2 is connected with the LAN port of R1, so the LAN port address of R1 is in the same network segment as the WAN port address of R2, the WAN port address of R1 and the WAN port of R3. In the same network segment.
So R1:
The destination address is 192.168.1.0, the mask is 255.255.255.0, and the next hop (gateway) is 192.168.0.100.
The destination address is 172.16.0.0, the mask is 255.255.0.0, and the next hop (gateway) is 10.1.1.3.
So R3:
The destination address is 192.168.0.0, the mask is 255.255.255.0, and the next hop is 10.1.1.2.
The destination address is 192.168.1.0, the mask is 255.255.255.0, and the next hop is 10.1.1.2.
If you don't understand the above, you can look at it from another angle:
For router R3, it can only see R1, but can't see R2, so for R3, the two routes R1 and R2 above can be summarized one by one.
The destination address is 192.168.0.0, the mask is 255.255.0.0, and the next hop is 10.1.1.2. This network segment contains all subnets of 192.168.0.0~192.168.255.0, including R1 and R2. This static route All packets with the destination IP in this range are forwarded to the 10.1.1.2 router R1. This classifies multiple sub-route entries into a total routing entry, which is called route summarization.
Why do you need to write the subnet mask accurately in the network?
On large routers, the routing table is often very long. Using route summarization can reduce the length of the routing table and improve router efficiency.
Of course, route summarization is not always effective, because the subnet is divided manually. Other network segments in the route summary may exist under other LANs. The transcript may be wrong, so we need to calculate the subnet mask in the actual project. It is very accurate, which is why WeChat has not recommended that we set the Class B URL to write the subnet mask directly to 255.255.0.0.
The route summary in the above example 3 can be set to be more precise. For 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.1.0, the same number of bits in the network bits have the first 23 bits. If you want to distinguish the two network segments by mask, you need to cover them. The code is set to 255.255.254.0 and is not recommended to be set to 255.255.0.0. This improved summary routing table should be written like this:
The destination address is 192.168.0.0, the subnet mask is 255.255.254.0, and the next hop is 10.1.1.2. This summary route will only contain two subnets, 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.0.1. This is an exact route. This will help the network to expand and maintain in the future.
Aluminum Die Casting Pulse Valve Dust Parts products
1. Die -cast Aluminium Pulse Valve Dust Parts products.
2. Strong bearing capacity.
3. Elaborated made to ex-change;
4 .Acceptable electric leakage;
5. Aluminum Die Casting suitable for communications, auto parts, lamp part series, water pump part series, power tool series, radiator part series, Aluminum Die Casting Pulse Valve Dust Parts and other series products.
Applications:
Aluminum Die Casting Pulse Valve Dust Parts also called diaphragm valve acts as a [switch" for compressed air in the dust clean blowing system for pulse bag filters. It is controlled by the electric signals from the pulse-jet control device. This system cleans the filter bags cluster by cluster with high-pressure blowing to keep the pressure resistance of the baghouse within a pre-set range, and thus ensure the processing capability and the dust-collecting efficiency of the baghouse.

pulse valves dust collectors products advantage
1. easy & fast to set up pulse valves dust collectors
2. Formaldehyde to release a quantity to reach national standard, health protection E0
3. Design novel, variety complete, fashion, ascending life style





