PLG Continuum Disc Dryer is a kind of high-efficiency transmission-type equipment for continuous drying. Its unique structure and WORKING PRINCIPLE determine its characteristics of high thermal efficiency, low energy consumption, small land occupation, simple configuration, convenient control and good operating environment. It is widely used in drying of industries of chemical, pharmaceutical, pesticide, food, forage, agricultural processing and so on. Disc Dryer,Plate Dryer,Lithium Carbonate Disc Dryer,Ternary Material Disc Dryer Changzhou Lead Machinery Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.leaddryer.com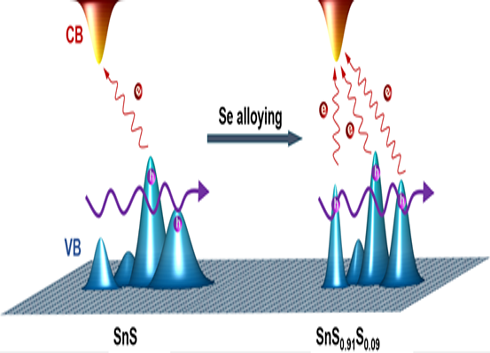
Science reports on the new development of Beihang thermoelectric materials research
[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] On September 27, 2019, Science magazine published a new development in the research of thermoelectric materials by Professor Zhao Lidong of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics: "High thermoelectric performance in low-cost SnS0.91Se0.09 crystals" It has discovered and utilized the evolution of multiple energy bands of tin sulfide (SnS) with temperature, and introduced the Se optimization to control the contradiction between effective mass and mobility. It is realized in SnS crystal materials with abundant reserves, low cost and environmental friendliness. High thermoelectric performance (Science, 2019, 365, 1418-1424, DOI: 10.1126/science.aax5123).
Thermoelectric materials have been the forefront and hotspot of international materials science and solid state physics research due to the mutual transformation of thermal energy and electrical energy in solid state. The outstanding thermoelectric materials are mainly concentrated on IV-VI compounds, such as GeTe, PbTe, PbSe, PbS, SnTe, SnSe and the like. Among these compounds, Ge and Te are rare, and Pb is highly toxic. Therefore, the development of inexpensive, non-toxic, high-performance thermoelectric materials is of great significance for improving the environmental characteristics and application value of thermoelectric materials.
The SnS structure is similar to the high-performance thermoelectric material SnSe, and the raw materials are more abundant and cheap, but the carrier mobility is lower, which limits the thermoelectric performance.
Thermoelectric materials not only require good electrical conductivity, but also require large temperature difference electromotive force, which is a contradiction between a pair of carrier concentration restrictions. This work is mainly focused on the optimization of temperature difference electromotive force and conductivity, that is, the synergistic regulation of effective mass m* and mobility μ (also a pair of contradictions). The degree of optimization of regulation can be measured by quality factor β, βâˆÎ¼(m* ) 3/2. Experimentally, the atomic occupancy information at different temperatures was obtained by the variable temperature synchrotron radiation test. Combined with the calculation of the electronic band structure, it was found that there are multiple valence bands interacting with temperature in the SnS material. That is, multiple valence bands undergo three processes of convergence (increasing effective mass and reducing mobility), intersection (convergence and separation), and separation (reducing effective mass and increasing mobility). Further research found that the evolution of this multivalent band with temperature can be enhanced by introducing Se in SnS, as shown in Figure 1. At the same time, it was found that the introduction of Se can also sharpen the multivalent band (reduce the effective mass and increase the mobility), and also promote more valence bands (the fourth valence band) to participate in the transmission (maintaining a large effective mass) ). After the introduction of Se, while the mobility is improved, a large effective mass is maintained, thereby obtaining a large quality factor β, which enables the SnS crystal to achieve high electrical transmission performance throughout the temperature range, even better than having a multi-price. SnSe crystal with transmission characteristics (Science, 2016, 351, 141-144). The maximum ZT value of the SnS crystal increased from ~1.0 to ~1.6, and the average ZT value in the entire temperature range reached ~1.25.