The piston type pressure gauge is designed according to the principle of hydrostatic balance and Pascal's law, which uses the principle that the force exerted on the piston by the pressure is balanced with the gravity of the code. Because of the gravity generated by the standard weight when balancing the load of the measured pressure, it is also called a static-weight piston type pressure gauge. Its structure is shown in Figure 3-8, which is mainly composed of a pressure generating part and a measuring part. (1) The pressure generation part. The pressure generating part mainly refers to the hand pump. The pressing screw rotates the screw rod, pushes the working piston (hand pump piston) to squeeze the working fluid, and transmits the pressure to be measured to the measuring piston through the working fluid. The working fluid is generally clean transformer oil or castor oil. (2) Measurement section. The mushroom code tray on the upper end of the measuring piston is placed with a load-bearing mushroom code. The piston is inserted into the piston cylinder, and the lower end is subjected to the pressure generated by the hand pump to squeeze the working fluid. PO acts on the hydraulic pressure at the lower end of the piston and the piston, the tray and the crucible. When the pressure generated by the mass of the code is balanced, the piston is lifted and stabilized at a certain position. At this time, the indication value of the pressure gauge is Where P is the measured pressure, Pa; Mass of m1, m2 and m3 pistons, trays and silicon codes, kg; A—the effective area of ​​the piston under pressure, m2; g—Gravitational acceleration of the location where the piston gauge is used, m/S2 2 error analysis A gravity acceleration effect The acceleration of gravity is related to the altitude and latitude of the location, and can be calculated by the following formula Where r - earth radius, calculated as r = 6371 x 103m; H—the altitude at which the pressure gauge is used, m; B air buoyancy effect If considering the effect of air on the buoyancy of the weight, the air buoyancy correction factor should be introduced in equation (3-20) as follows Where P1, P2 - the density of local air and weight, kg / m3 It can be seen that if the influence of air buoyancy is neglected, the measured pressure value will be made larger. Effect of temperature change When the ambient temperature is not 20 ° C, the following temperature correction factor should be introduced in formula (3-20) In the formula, a1, a2--the linear expansion coefficient of the piston and piston cylinder material, °C-1 T--the ambient temperature at work, °C; Effective area of ​​piston at AO--20 °C, m2 B—the rate of change of the effective area of ​​the piston for every change of 9.88065 Pa, Pa-1 When the piston and piston cylinder materials are the same Where E - the modulus of elasticity of the piston and piston cylinder material, Pa; u—Poisson's ratio of piston to piston cylinder material; r, R-piston, piston cylinder radius, m Precautions for use (1) Before use, check whether the oil passages are unblocked. 'The seals should be tightened, and there should be no blockage or oil leakage. (2) The part of the piston entering the piston cylinder should be equal to 2/3-3/4 of the total length of the piston. (3) The number of the piston pressure gauge should be the same as the special cutting code number. It is forbidden to exchange the special brick codes of multiple pressure gauges. In plus Avoid sudden rise and fall of the piston when reducing the brick code. The correct way is to close the valve to the piston before adding or subtracting the weight. After confirming that the addition and subtraction code is correct, open the valve. (4) The clearance between the piston and the cylinder is very small, so the shear force generated by the oil between the two along the axial direction will have an impact on the accurate measurement. In order to reduce this kind of simple friction, the piston can be gently rotated when the star is measured. (5) The piston should be in a vertical position, that is, the piston pressure gauge chassis should use the blisters on it to adjust it to a level. (6) When used as a standard instrument for testing pressure gauges, the comprehensive error of the pressure gauge should not exceed 1/3 of the absolute value of the basic error of the instrument to be inspected. The range of the pressure gauge should be 10% to 100% of the upper limit of the star. When less than 10%, the pressure gauge should be replaced. (7) The operation steps when verifying or verifying other pressure gauges should be detailed in the relevant instruction manual; when verifying the vacuum gauge, the operation steps are slightly different and should be noted. Hubei ruiyate Automobile Co.,Ltd , https://www.nbruiyate-automobile.com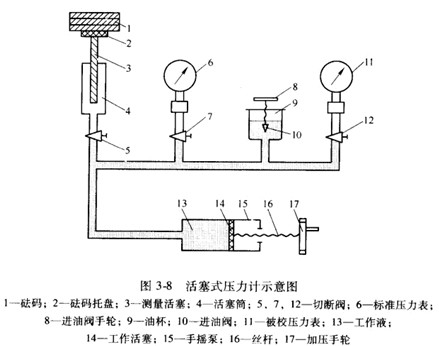

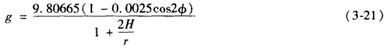
 - The latitude of the location where the gauge is used.
- The latitude of the location where the gauge is used. 

